Dubbo SPI扩展机制源码详解(基于2.7.10)
一. 概述
本文主要分享 Dubbo 的拓展机制 SPI。
想要理解 Dubbo ,理解 Dubbo SPI 是非常必须的。在 Dubbo 中,提供了大量的拓展点,基于 Dubbo SPI 机制加载
Dubbo SPI官方文档:Dubbo SPI 概述 | Apache Dubbo
本文基于 Dubbo 2.7.10 版本源码
二. Dubbo SPI特性
在看具体的 Dubbo SPI 实现之前,我们先理解 Dubbo SPI 产生的背景:
Dubbo 的扩展点加载从 JDK 标准的 SPI (Service Provider Interface) 扩展点发现机制加强而来。
Dubbo 改进了 JDK 标准的 SPI 的以下问题:
- JDK 标准的 SPI 会一次性实例化扩展点所有实现,如果有扩展实现初始化很耗时,但如果没用上也加载,会很浪费资源。
- 如果扩展点加载失败,连扩展点的名称都拿不到了。比如:JDK 标准的 ScriptEngine,通过 getName() 获取脚本类型的名称,但如果 RubyScriptEngine 因为所依赖的 jruby.jar 不存在,导致 RubyScriptEngine 类加载失败,这个失败原因被吃掉了,和 ruby 对应不起来,当用户执行 ruby 脚本时,会报不支持 ruby,而不是真正失败的原因。
- 增加了对扩展点 IoC 和 AOP 的支持,一个扩展点可以直接 setter 注入其它扩展点。
用户能够基于 Dubbo 提供的扩展能力,很方便基于自身需求扩展其他协议、过滤器、路由等。下面介绍下 Dubbo 扩展能力的特性。
- 按需加载。Dubbo 的扩展能力不会一次性实例化所有实现,而是用那个扩展类则实例化那个扩展类,减少资源浪费。
- 增加扩展类的 IOC 能力。Dubbo 的扩展能力并不仅仅只是发现扩展服务实现类,而是在此基础上更进一步,如果该扩展类的属性依赖其他对象,则 Dubbo 会自动的完成该依赖对象的注入功能。
- 增加扩展类的 AOP 能力。Dubbo 扩展能力会自动的发现扩展类的包装类,完成包装类的构造,增强扩展类的功能。
- 具备动态选择扩展实现的能力。Dubbo 扩展会基于参数,在运行时动态选择对应的扩展类,提高了 Dubbo 的扩展能力。
- 可以对扩展实现进行排序。能够基于用户需求,指定扩展实现的执行顺序。
- 提供扩展点的 Adaptive 能力。该能力可以使的一些扩展类在 consumer 端生效,一些扩展类在 provider 端生效。
从 Dubbo 扩展的设计目标可以看出,Dubbo 实现的一些例如动态选择扩展实现、IOC、AOP 等特性,能够为用户提供非常灵活的扩展能力。
三. 代码结构
Dubbo SPI 在 dubbo-common 的 org.apache.dubbo.common.extension 包实现,如下图所示:
四. ExtensionLoader
org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.ExtensionLoader ,拓展加载器。这是 Dubbo SPI 的核心。
4.1 属性
/**
* 拓展加载器集合
*/
private static final ConcurrentMap<Class<?>, ExtensionLoader<?>> EXTENSION_LOADERS = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64);
/**
* 拓展加载器集合
* key:拓展接口
*/
private static final ConcurrentMap<Class<?>, Object> EXTENSION_INSTANCES = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64);
/**
* 拓展接口
*/
private final Class<?> type;
/**
* 对象工厂
*
* 用于调用 {@link #injectExtension(Object)} 方法,向拓展对象注入依赖属性。
*
* 例如,StubProxyFactoryWrapper 中有 `Protocol protocol` 属性。
*/
private final ExtensionFactory objectFactory;
/**
* 缓存的拓展名与拓展类的映射。
*
* 和 {@link #cachedClasses} 的 KV 对调。
*
* 通过 {@link #loadExtensionClasses} 加载
*/
private final ConcurrentMap<Class<?>, String> cachedNames = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 缓存的拓展实现类集合。
*
* 不包含如下两种类型:
* 1. 自适应拓展实现类。例如 AdaptiveExtensionFactory
* 2. 带唯一参数为拓展接口的构造方法的实现类,或者说拓展 Wrapper 实现类。例如,ProtocolFilterWrapper 。
* 拓展 Wrapper 实现类,会添加到 {@link #cachedWrapperClasses} 中
*
* 通过 {@link #loadExtensionClasses} 加载
*/
private final Holder<Map<String, Class<?>>> cachedClasses = new Holder<>();
/**
* 拓展名与 @Activate 的映射
*
* 例如,AccessLogFilter。
*
* 用于 {@link #getActivateExtension(URL, String)}
*/
private final Map<String, Object> cachedActivates = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 缓存的拓展对象集合
*
* key:拓展名
* value:拓展对象
*
* 例如,Protocol 拓展
* key:dubbo value:DubboProtocol
* key:injvm value:InjvmProtocol
*
* 通过 {@link #loadExtensionClasses} 加载
*/
private final ConcurrentMap<String, Holder<Object>> cachedInstances = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 缓存的自适应( Adaptive )拓展对象
*/
private final Holder<Object> cachedAdaptiveInstance = new Holder<>();
/**
* 缓存的自适应拓展对象的类
*
* {@link #getAdaptiveExtensionClass()}
*/
private volatile Class<?> cachedAdaptiveClass = null;
/**
* 缓存的默认拓展名
*
* 通过 {@link SPI} 注解获得
*/
private String cachedDefaultName;
/**
* 创建 {@link #cachedAdaptiveInstance} 时发生的异常。
*
* 发生异常后,不再创建,参见 {@link #createAdaptiveExtension()}
*/
private volatile Throwable createAdaptiveInstanceError;
/**
* 拓展 Wrapper 实现类集合
*
* 带唯一参数为拓展接口的构造方法的实现类
*
* 通过 {@link #loadExtensionClasses} 加载
*/
private Set<Class<?>> cachedWrapperClasses;
/**
* 拓展名 与 加载对应拓展类发生的异常 的 映射
*
* key:拓展名
* value:异常
*
* 在 {@link #loadFile(Map, String)} 时,记录
*/
private Map<String, IllegalStateException> exceptions = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private static volatile LoadingStrategy[] strategies = loadLoadingStrategies();
我们将属性分成了两类:1)静态属性;2)对象属性。这是为啥呢?
- 【静态属性】一方面,ExtensionLoader 是 ExtensionLoader 的管理容器。一个拓展( 拓展接口 )对应一个 ExtensionLoader 对象。例如,Protocol 和 Filter 分别对应一个 ExtensionLoader 对象。
- 【对象属性】另一方面,一个拓展通过其 ExtensionLoader 对象,加载它的拓展实现们。我们会发现多个属性都是 “cached” 开头。ExtensionLoader 考虑到性能和资源的优化,读取拓展配置后,会首先进行缓存。等到 Dubbo 代码真正用到对应的拓展实现时,进行拓展实现的对象的初始化。并且,初始化完成后,也会进行缓存。也就是说:
- 缓存加载的拓展配置
- 缓存创建的拓展实现对象
4.2 获得拓展配置
4.2.1 getExtensionClasses
/**
* 缓存的拓展实现类集合。
*
* 不包含如下两种类型:
* 1. 自适应拓展实现类。例如 AdaptiveExtensionFactory
* 2. 带唯一参数为拓展接口的构造方法的实现类,或者说拓展 Wrapper 实现类。例如,ProtocolFilterWrapper 。
* 拓展 Wrapper 实现类,会添加到 {@link #cachedWrapperClasses} 中
*
* 通过 {@link #loadExtensionClasses} 加载
*/
private final Holder<Map<String, Class<?>>> cachedClasses = new Holder<>();
/**
* 缓存的自适应拓展对象的类
*
* {@link #getAdaptiveExtensionClass()}
*/
private volatile Class<?> cachedAdaptiveClass = null;
/**
* 拓展 Wrapper 实现类集合
*
* 带唯一参数为拓展接口的构造方法的实现类
*
* 通过 {@link #loadExtensionClasses} 加载
*/
private Set<Class<?>> cachedWrapperClasses;
/**
* 获得拓展实现
*
* @return 拓展实现类数组
*/
private Map<String, Class<?>> getExtensionClasses() {
// 从缓存中,获得拓展实现类数组
Map<String, Class<?>> classes = cachedClasses.get();
if (classes == null) {
synchronized (cachedClasses) {
classes = cachedClasses.get();
if (classes == null) {
// 从配置文件中,加载拓展实现类数组
classes = loadExtensionClasses();
// 设置到缓存中
cachedClasses.set(classes);
}
}
}
return classes;
}
- cachedClasses属性,缓存的拓展实现类集合。它不包含如下两种类型的拓展实现:
- 自适应拓展实现类。例如 AdaptiveExtensionFactory 。
- 拓展 Adaptive 实现类,会添加到
cachedAdaptiveClass属性中。
- 拓展 Adaptive 实现类,会添加到
- 带唯一参数为拓展接口的构造方法的实现类,或者说拓展 Wrapper 实现类。例如,ProtocolFilterWrapper 。
- 拓展 Wrapper 实现类,会添加到
cachedWrapperClasses属性中。
- 拓展 Wrapper 实现类,会添加到
- 总结来说,
cachedClasses+cachedAdaptiveClass+cachedWrapperClasses才是完整缓存的拓展实现类的配置。
- 自适应拓展实现类。例如 AdaptiveExtensionFactory 。
4.2.2 loadExtensionClasses
private Map<String, Class<?>> loadExtensionClasses() {
// 加载默认的拓展名
cacheDefaultExtensionName();
Map<String, Class<?>> extensionClasses = new HashMap<>();
// 循环加载策略,加载对应的拓展实现
for (LoadingStrategy strategy : strategies) {
loadDirectory(extensionClasses, strategy.directory(), type.getName(), strategy.preferExtensionClassLoader(), strategy.overridden(), strategy.excludedPackages());
// 为了兼容 2.7 之前的老版本。在2.7之前,Dubbo还未进入Apache孵化,包名还是Alibaba
loadDirectory(extensionClasses, strategy.directory(), type.getName().replace("org.apache", "com.alibaba"), strategy.preferExtensionClassLoader(), strategy.overridden(), strategy.excludedPackages());
}
return extensionClasses;
}
第一步:加载默认的扩展名
第二步:遍历加载策略数组,去加载不同文件夹下的扩展。
strategies属性是在启动时,在 loadLoadingStrategies 方法中通过 Java SPI 加载的 LoadingStrategy 接口的实现类。
private static volatile LoadingStrategy[] strategies = loadLoadingStrategies();
private static LoadingStrategy[] loadLoadingStrategies() {
return stream(load(LoadingStrategy.class).spliterator(), false)
.sorted()
.toArray(LoadingStrategy[]::new);
}
它会读取 META-INF/services 下的 org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.LoadingStrategy 文件中注册的实现类:
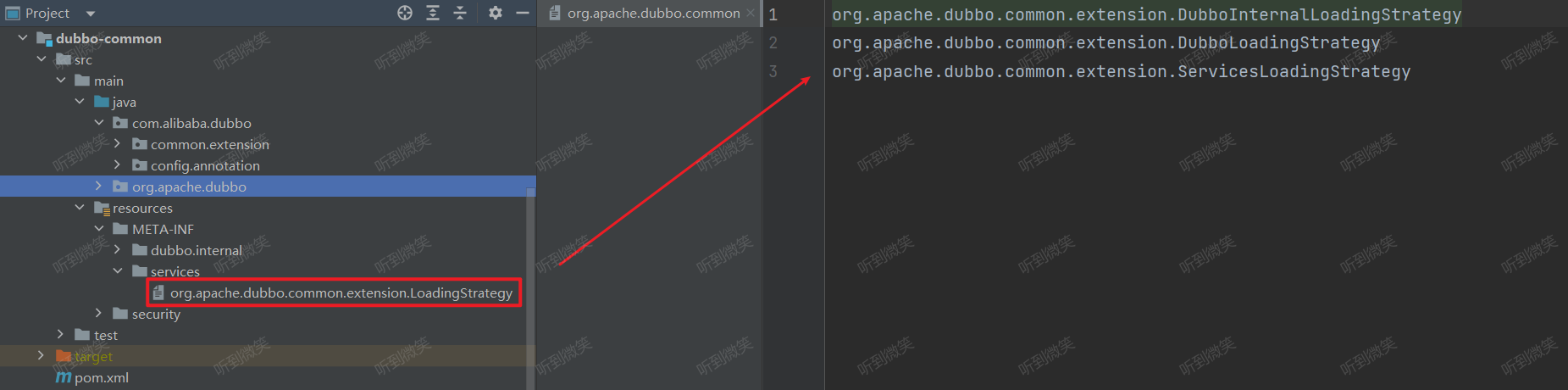
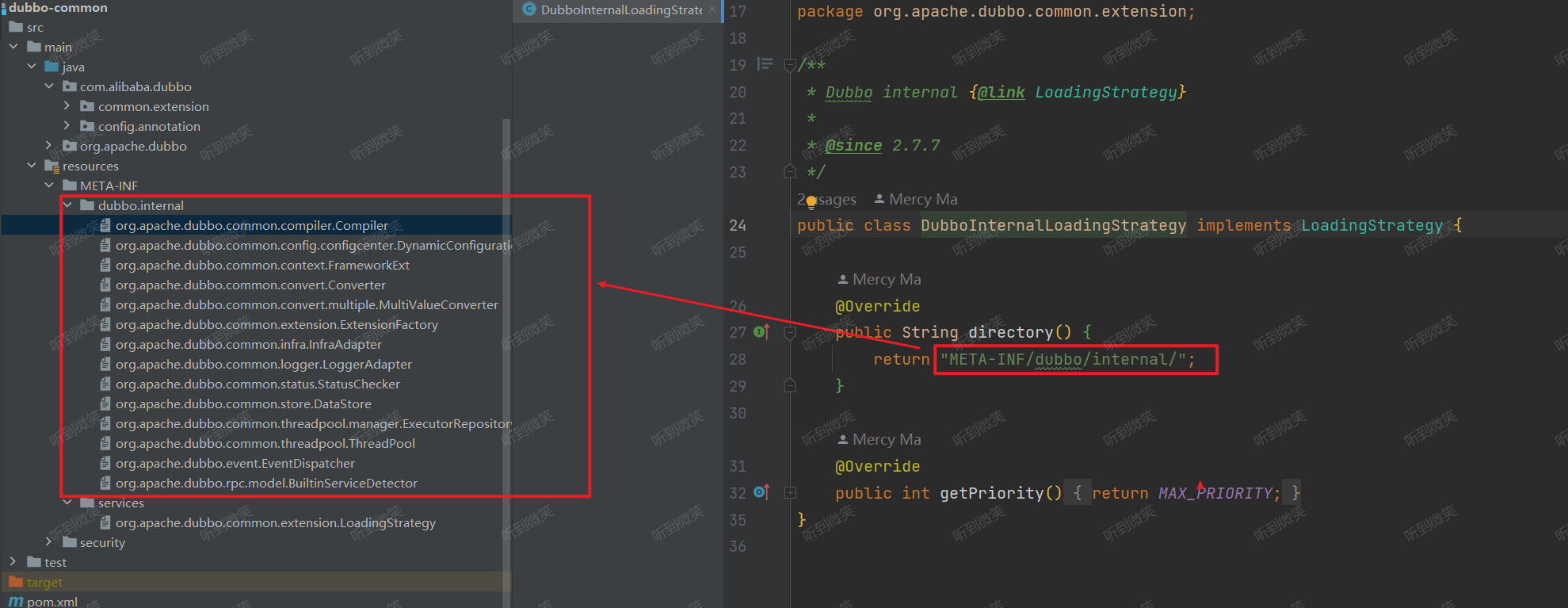
这些实现类中会指定,需要加载的拓展的配置文件路径:
public class DubboInternalLoadingStrategy implements LoadingStrategy {
// 加载 META-INF/dubbo/internal/ 下的扩展实现
@Override
public String directory() {
return "META-INF/dubbo/internal/";
}
@Override
public int getPriority() {
return MAX_PRIORITY;
}
}
loadDirectory方法
private void loadDirectory(Map<String, Class<?>> extensionClasses, String dir, String type,
boolean extensionLoaderClassLoaderFirst, boolean overridden, String... excludedPackages) {
// 获得完整的文件名( 相对路径 )。例如:"META-INF/dubbo/internal/com.alibaba.dubbo.common.extension.ExtensionFactory" 。
String fileName = dir + type;// 第4行
try {
// 获得文件名对应的所有文件数组
Enumeration<java.net.URL> urls = null;
ClassLoader classLoader = findClassLoader();
// try to load from ExtensionLoader's ClassLoader first
if (extensionLoaderClassLoaderFirst) {
ClassLoader extensionLoaderClassLoader = ExtensionLoader.class.getClassLoader();
if (ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader() != extensionLoaderClassLoader) {
urls = extensionLoaderClassLoader.getResources(fileName);
}
}
if (urls == null || !urls.hasMoreElements()) { // 第 18 行
if (classLoader != null) {
urls = classLoader.getResources(fileName);
} else {
urls = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(fileName);
}
} // 第 24 行
if (urls != null) {
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) { // 第 27 行
java.net.URL resourceURL = urls.nextElement();
// 加载指定配置文件(resourceURL)下的实现
loadResource(extensionClasses, classLoader, resourceURL, overridden, excludedPackages);
}
} // 第 32 行
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Exception occurred when loading extension class (interface: " +
type + ", description file: " + fileName + ").", t);
}
}
-
第 4 行:获得完整的文件名( 相对路径 )。例如:
"META-INF/dubbo/internal/com.alibaba.dubbo.common.extension.ExtensionFactory"。 -
第 18 至 24 行:获得文件名对应的所有文件 URL 数组。例如:

-
第 27 至 32 行:遍历逐个文件。
loadResource方法
private void loadResource(Map<String, Class<?>> extensionClasses, ClassLoader classLoader,
java.net.URL resourceURL, boolean overridden, String... excludedPackages) {
try {
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(resourceURL.openStream(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8))) {
String line;
String clazz = null;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
// 去除 #注释
final int ci = line.indexOf('#');
if (ci >= 0) {
line = line.substring(0, ci);
}
line = line.trim();
if (line.length() > 0) {
try {
// 拆分,key=value 的配置格式
String name = null;
int i = line.indexOf('=');
if (i > 0) {
name = line.substring(0, i).trim();
clazz = line.substring(i + 1).trim();
} else {
// Dubbo SPI 会兼容 Java SPI 的配置格式,那么按照此处的解析方式,name 会为空。这种情况下,拓展名会自动生成
clazz = line;
}
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(clazz) && !isExcluded(clazz, excludedPackages)) {
// 加载配置文件配置拓展的实现类
loadClass(extensionClasses, resourceURL, Class.forName(clazz, true, classLoader), name, overridden);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
IllegalStateException e = new IllegalStateException("Failed to load extension class (interface: " + type + ", class line: " + line + ") in " + resourceURL + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
exceptions.put(line, e);
}
}
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Exception occurred when loading extension class (interface: " +
type + ", class file: " + resourceURL + ") in " + resourceURL, t);
}
}
- 第 7 行:进入文件内部,逐行遍历。
loadClass方法
private void loadClass(Map<String, Class<?>> extensionClasses, java.net.URL resourceURL, Class<?> clazz, String name,
boolean overridden) throws NoSuchMethodException {
// 判断拓展实现,是否实现拓展接口
if (!type.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Error occurred when loading extension class (interface: " +
type + ", class line: " + clazz.getName() + "), class "
+ clazz.getName() + " is not subtype of interface.");
}
// 检测目标类上是否有 Adaptive 注解
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Adaptive.class)) {
// 缓存自适应拓展对象的类到 `cachedAdaptiveClass`
cacheAdaptiveClass(clazz, overridden);
} else if (isWrapperClass(clazz)) {
// 检测 clazz 是否是 Wrapper 类型
// 缓存拓展 Wrapper 实现类到 `cachedWrapperClasses`
cacheWrapperClass(clazz);
} else {
// 程序进入此分支,表明 clazz 是一个普通的拓展类
clazz.getConstructor();
// 未配置拓展名,自动生成。例如,DemoFilter 为 demo 。主要用于兼容 Java SPI 的配置。
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(name)) {
// 如果 name 为空,则尝试从 Extension 注解中获取 name,或使用小写的类名作为 name
name = findAnnotationName(clazz);
if (name.length() == 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No such extension name for the class " + clazz.getName() + " in the config " + resourceURL);
}
}
// 获得拓展名,可以是数组,有多个拓展名。
String[] names = NAME_SEPARATOR.split(name);
if (ArrayUtils.isNotEmpty(names)) {
// 缓存 @Activate 到 `cachedActivates` 。
cacheActivateClass(clazz, names[0]);
for (String n : names) {
// 缓存到 `cachedNames`
cacheName(clazz, n);
// 若 isWrapperClass 方法获取构造方法失败,则代表是普通的拓展实现类,缓存到 extensionClasses 变量中
saveInExtensionClass(extensionClasses, clazz, n, overridden);
}
}
}
}
4.3 获得拓展加载器
在 Dubbo 的代码里,常常能看到如下的代码:
ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getExtension(name)
4.3.1 getExtensionLoader
/**
* 根据拓展点的接口,获得拓展加载器
*
* @param type 接口
* @param <T> 泛型
* @return 加载器
*/
public static <T> ExtensionLoader<T> getExtensionLoader(Class<T> type) {
if (type == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension type == null");
}
// 必须是接口
if (!type.isInterface()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension type (" + type + ") is not an interface!");
}
// 必须包含 @SPI 注解
if (!withExtensionAnnotation(type)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension type (" + type +
") is not an extension, because it is NOT annotated with @" + SPI.class.getSimpleName() + "!");
}
// 获得接口对应的拓展点加载器
ExtensionLoader<T> loader = (ExtensionLoader<T>) EXTENSION_LOADERS.get(type);
if (loader == null) {
// 若不存在,则创建 ExtensionLoader 对象,并添加到 EXTENSION_LOADERS。
EXTENSION_LOADERS.putIfAbsent(type, new ExtensionLoader<T>(type));
loader = (ExtensionLoader<T>) EXTENSION_LOADERS.get(type);
}
return loader;
}
4.3.2 构造方法
构造方法,代码如下:
/**
* 拓展接口。
* 例如,Protocol
*/
private final Class<?> type;
/**
* 对象工厂
*
* 用于调用 {@link #injectExtension(Object)} 方法,向拓展对象注入依赖属性。
*
* 例如,StubProxyFactoryWrapper 中有 `Protocol protocol` 属性。
*/
private final ExtensionFactory objectFactory;
private ExtensionLoader(Class<?> type) {
this.type = type;
objectFactory = (type == ExtensionFactory.class ? null : ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ExtensionFactory.class).getAdaptiveExtension()); // 第 17 行
}
objectFactory属性,对象工厂,功能上和 Spring IOC 一致。- 用于调用
#injectExtension(instance)方法时,向创建的拓展注入其依赖的属性。例如,CacheFilter.cacheFactory属性。 - 第 17 行:当拓展接口非 ExtensionFactory 时(如果不加这个判断,会是一个死循环),调用
ExtensionLoader#getAdaptiveExtension()方法,获得 ExtensionFactory 拓展接口的自适应拓展实现对象。为什么呢?在 后文详细解释。
- 用于调用
4.4 获得指定拓展对象
在 Dubbo 的代码里,常常能看到如下的代码:
ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getExtension(name)
4.4.1 getExtension
/**
* 返回指定名字的扩展对象。如果指定名字的扩展不存在,则抛异常 {@link IllegalStateException}.
*
* @param name 拓展名
* @return 拓展对象
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T getExtension(String name) {
return getExtension(name, true);
}
public T getExtension(String name, boolean wrap) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(name)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension name == null");
}
// 查找 默认的 拓展对象
if ("true".equals(name)) {
return getDefaultExtension();
}
// 从 缓存中 获得对应的拓展对象
final Holder<Object> holder = getOrCreateHolder(name);
Object instance = holder.get();
if (instance == null) {
synchronized (holder) {
instance = holder.get();
// 从 缓存中 未获取到,进行创建缓存对象。
if (instance == null) {
instance = createExtension(name, wrap);
// 设置创建对象到缓存中
holder.set(instance);
}
}
}
return (T) instance;
}
4.4.2 createExtension
#createExtension(name) 方法,创建拓展名的拓展对象,并缓存。代码如下:
/**
* 创建拓展名的拓展对象,并缓存。
*
* @param name 拓展名
* @return 拓展对象
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private T createExtension(String name, boolean wrap) {
// 获得拓展名对应的拓展实现类
Class<?> clazz = getExtensionClasses().get(name);
if (clazz == null) {
throw findException(name);
}
try {
// 从缓存中,获得拓展对象。
T instance = (T) EXTENSION_INSTANCES.get(clazz);
if (instance == null) {
// 当缓存不存在时,创建拓展对象,并添加到缓存中。
EXTENSION_INSTANCES.putIfAbsent(clazz, clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance());
instance = (T) EXTENSION_INSTANCES.get(clazz);
}
// 注入依赖的属性
injectExtension(instance);
if (wrap) {
List<Class<?>> wrapperClassesList = new ArrayList<>();
if (cachedWrapperClasses != null) {
wrapperClassesList.addAll(cachedWrapperClasses);
wrapperClassesList.sort(WrapperComparator.COMPARATOR);
Collections.reverse(wrapperClassesList);
}
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(wrapperClassesList)) {
for (Class<?> wrapperClass : wrapperClassesList) {
Wrapper wrapper = wrapperClass.getAnnotation(Wrapper.class);
if (wrapper == null
|| (ArrayUtils.contains(wrapper.matches(), name) && !ArrayUtils.contains(wrapper.mismatches(), name))) {
// 创建 Wrapper 拓展对象
instance = injectExtension((T) wrapperClass.getConstructor(type).newInstance(instance));
}
}
}
}
// 实例初始化
initExtension(instance);
return instance;
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Extension instance (name: " + name + ", class: " +
type + ") couldn't be instantiated: " + t.getMessage(), t);
}
}
Wrapper 类同样实现了扩展点接口,但是 Wrapper 不是扩展点的真正实现。它的用途主要是用于从 ExtensionLoader 返回扩展点时,包装在真正的扩展点实现外。即从 ExtensionLoader 中返回的实际上是 Wrapper 类的实例,Wrapper 持有了实际的扩展点实现类。
扩展点的 Wrapper 类可以有多个,也可以根据需要新增。
通过 Wrapper 类可以把所有扩展点公共逻辑移至 Wrapper 中。新加的 Wrapper 在所有的扩展点上添加了逻辑,有些类似 AOP,即 Wrapper 代理了扩展点。
- 例如:[ListenerExporterWrapper、ProtocolFilterWrapper 。
4.4.3 injectExtension注入依赖
private T injectExtension(T instance) {
if (objectFactory == null) {
return instance;
}
try {
for (Method method : instance.getClass().getMethods()) {
if (!isSetter(method)) {
continue;
}
/**
* Check {@link DisableInject} to see if we need auto injection for this property
*/
if (method.getAnnotation(DisableInject.class) != null) {
continue;
}
// 获得属性的类型
Class<?> pt = method.getParameterTypes()[0];
if (ReflectUtils.isPrimitives(pt)) {
continue;
}
try {
// 获取setter的属性名,例如:setVersion,返回"version"
String property = getSetterProperty(method);
// 获得属性值
Object object = objectFactory.getExtension(pt, property); // 第 28 行
// 设置属性值
if (object != null) {
method.invoke(instance, object);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Failed to inject via method " + method.getName()
+ " of interface " + type.getName() + ": " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
return instance;
}
- 第 28 行:获得属性值。注意,此处虽然调用的是
ExtensionFactory#getExtension(type, name)方法,实际获取的不仅仅是拓展对象,也可以是 Spring Bean 对象。
4.5 获得自适应的拓展对象
在 Dubbo 的代码里,常常能看到如下的代码:
ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getAdaptiveExtension();
友情提示,胖友先看下 「6. Adaptive」 的内容再回到此处。
Dubbo 自适应拓展的作用可以参考:SPI 自适应拓展 | Apache Dubbo
4.5.1 getAdaptiveExtension
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T getAdaptiveExtension() {
// 从缓存中,获得自适应拓展对象
Object instance = cachedAdaptiveInstance.get();
if (instance == null) {
// 若之前创建报错,则抛出异常 IllegalStateException
if (createAdaptiveInstanceError != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to create adaptive instance: " +
createAdaptiveInstanceError.toString(),
createAdaptiveInstanceError);
}
synchronized (cachedAdaptiveInstance) {
instance = cachedAdaptiveInstance.get();
if (instance == null) {
try {
// 创建自适应拓展对象
instance = createAdaptiveExtension();
// 设置到缓存
cachedAdaptiveInstance.set(instance);
} catch (Throwable t) {
// 记录异常
createAdaptiveInstanceError = t;
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to create adaptive instance: " + t.toString(), t);
}
}
}
}
return (T) instance;
}
4.5.2 createAdaptiveExtension
/**
* 创建自适应拓展对象
*
* @return 拓展对象
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private T createAdaptiveExtension() {
try {
// 创建自适应拓展对象,并注入属性
return injectExtension((T) getAdaptiveExtensionClass().newInstance());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Can't create adaptive extension " + type + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
4.5.3 getAdaptiveExtensionClass
#getAdaptiveExtensionClass() 方法,获得自适应拓展类。代码如下:
/**
* @return 自适应拓展类
*/
private Class<?> getAdaptiveExtensionClass() {
getExtensionClasses();
// cachedAdaptiveClass 存在 直接返回
if (cachedAdaptiveClass != null) {
return cachedAdaptiveClass;
}
// 自动生成自适应拓展的代码实现,并编译后返回该类。
return cachedAdaptiveClass = createAdaptiveExtensionClass();
}
4.5.4 createAdaptiveExtensionClass
/**
* 自动生成自适应拓展的代码实现,并编译后返回该类。
*
* @return 类
*/
private Class<?> createAdaptiveExtensionClass() {
// 自动生成自适应拓展的代码实现的字符串
String code = new AdaptiveClassCodeGenerator(type, cachedDefaultName).generate();// 第 5 行
// 编译代码,并返回该类
ClassLoader classLoader = findClassLoader();
org.apache.dubbo.common.compiler.Compiler compiler = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(org.apache.dubbo.common.compiler.Compiler.class).getAdaptiveExtension();
return compiler.compile(code, classLoader);
}
第 5 行会生成自适应拓展的代码实现,然后会编译字符串生成 Class。我们以 org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster 接口为例,它生成的自适应拓展实现如下:
package org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.ExtensionLoader;
public class Cluster$Adaptive implements org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster {
public org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster getCluster(
java.lang.String arg0) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"The method public static org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster.getCluster(java.lang.String) of interface org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster is not adaptive method!");
}
public org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster getCluster(
java.lang.String arg0, boolean arg1) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"The method public static org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster.getCluster(java.lang.String,boolean) of interface org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster is not adaptive method!");
}
public org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker join(
org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory arg0)
throws org.apache.dubbo.rpc.RpcException {
if (arg0 == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory argument == null");
}
if (arg0.getUrl() == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory argument getUrl() == null");
}
// 获取请求的URL
org.apache.dubbo.common.URL url = arg0.getUrl();
// 获取URL上的 cluster 参数,如果没有该参数,则默认为 failover
String extName = url.getParameter("cluster", "failover");
if (extName == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Failed to get extension (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster) name from url (" +
url.toString() + ") use keys([cluster])");
}
// 根据URL指定的集群容错策略,加载对应的Cluster实现类,并调用对应实现的join方法
org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster extension = (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster) ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster.class)
.getExtension(extName);
return extension.join(arg0);
}
}
生成的代码中,就是自适应拓展实现的核心,它会根据请求URL的参数,去动态加载对应的Cluster实现,完成不同的集群容错策略。
4.6 获得激活的拓展对象数组
在 Dubbo 的代码里,看到使用代码如下:
List<Filter> filters = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Filter.class).getActivateExtension(invoker.getUrl(), key, group);
4.6.1 getActivateExtension
#getActivateExtension(url, key, group) 方法,获得符合自动激活条件的拓展对象数组。
/**
* This is equivalent to {@code getActivateExtension(url, url.getParameter(key).split(","), null)}
* 获得符合自动激活条件的拓展对象数组
* @param url url
* @param key url parameter key which used to get extension point names
* @param group group
* @return extension list which are activated.
* @see #getActivateExtension(org.apache.dubbo.common.URL, String[], String)
*/
public List<T> getActivateExtension(URL url, String key, String group) {
// 从 Dubbo URL 获得参数值
String value = url.getParameter(key);
// 获得符合自动激活条件的拓展对象数组
return getActivateExtension(url, StringUtils.isEmpty(value) ? null : COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(value), group);
}
/**
* Get activate extensions.
* 获得符合自动激活条件的拓展对象数组
* @param url url
* @param values extension point names
* @param group group
* @return extension list which are activated
* @see org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.Activate
*/
public List<T> getActivateExtension(URL url, String[] values, String group) {
List<T> activateExtensions = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> names = values == null ? new ArrayList<>(0) : asList(values);
// 处理自动激活的拓展对象们
// 判断不存在配置 `"-name"` 。例如,<dubbo:service filter="-default" /> ,代表移除所有默认过滤器。
if (!names.contains(REMOVE_VALUE_PREFIX + DEFAULT_KEY)) {
// 获得拓展实现类数组
getExtensionClasses();
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : cachedActivates.entrySet()) {
String name = entry.getKey();
Object activate = entry.getValue();
String[] activateGroup, activateValue;
if (activate instanceof Activate) {
activateGroup = ((Activate) activate).group();
activateValue = ((Activate) activate).value();
} else if (activate instanceof com.alibaba.dubbo.common.extension.Activate) {
activateGroup = ((com.alibaba.dubbo.common.extension.Activate) activate).group();
activateValue = ((com.alibaba.dubbo.common.extension.Activate) activate).value();
} else {
continue;
}
if (isMatchGroup(group, activateGroup) // 匹配分组
&& !names.contains(name) // 不包含在自定义配置里。如果包含,会在下面的代码处理。
&& !names.contains(REMOVE_VALUE_PREFIX + name) // 判断是否配置移除。例如 <dubbo:service filter="-monitor" />,则 MonitorFilter 会被移除
&& isActive(activateValue, url)) { // 判断是否激活
activateExtensions.add(getExtension(name));
}
}
// 排序
activateExtensions.sort(ActivateComparator.COMPARATOR);
}
// 处理自定义配置的拓展对象们。例如在 <dubbo:service filter="demo" /> ,代表需要加入 DemoFilter 。
List<T> loadedExtensions = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < names.size(); i++) {
String name = names.get(i);
if (!name.startsWith(REMOVE_VALUE_PREFIX)
&& !names.contains(REMOVE_VALUE_PREFIX + name)) {
// 将配置的自定义在自动激活的拓展对象们前面。例如,<dubbo:service filter="demo,default,demo2" /> ,则 DemoFilter 就会放在默认的过滤器前面。
if (DEFAULT_KEY.equals(name)) {
if (!loadedExtensions.isEmpty()) {
activateExtensions.addAll(0, loadedExtensions);
loadedExtensions.clear();
}
} else {
// 获得拓展对象
loadedExtensions.add(getExtension(name));
}
}
}
// 添加到结果集
if (!loadedExtensions.isEmpty()) {
activateExtensions.addAll(loadedExtensions);
}
return activateExtensions;
}
五. @SPI
org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.SPI,扩展点接口的标识。代码如下:
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
public @interface SPI {
/**
* default extension name
*/
String value() default "";
}
-
value,默认拓展实现类的名字。例如,Protocol 拓展接口,代码如下:@SPI("dubbo") public interface Protocol { // ... 省略代码 }- 其中
"dubbo"指的是 DubboProtocol 做为 Protocol 默认的拓展实现类。
- 其中
六. @Adaptive
org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.Adaptive,自适应拓展信息的标记。代码如下:
package org.apache.dubbo.common.extension;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.URL;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* Provide helpful information for {@link ExtensionLoader} to inject dependency extension instance.
*
* @see ExtensionLoader
* @see URL
*/
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface Adaptive {
/**
* 从 {@link URL }的 Key 名,对应的 Value 作为要 Adapt 成的 Extension 名。
* <p>
* 如果 {@link URL} 这些 Key 都没有 Value ,使用 缺省的扩展(注解 @SPI 设置的值)。<br>
* 比如,@Adptive({"key1", "key2"}),表示
* <ol>
* <li>先在URL上找key1的Value作为要Adapt成的Extension名;
* <li>key1没有Value,则使用key2的Value作为要Adapt成的Extension名。
* <li>key2没有Value,使用默认的扩展。
* <li>如果没有设定缺省扩展,则方法调用会抛出{@link IllegalStateException}。
* </ol>
* <p>
* 如果参数名为空,则根据接口的类名生成一个默认的参数名,其规则是 接口名称的全小写。
* 例如 org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Protocol 接口,默认的参数名是:protocol
* 详细逻辑参考:org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.AdaptiveClassCodeGenerator#getMethodAdaptiveValue
*
* @see SPI#value()
*/
String[] value() default {};
}
@Adaptive注解,可添加类或方法上,分别代表了两种不同的使用方式。
友情提示:一个拓展接口,有且仅有一个 Adaptive 拓展实现类。
- 第一种,标记在类上,代表手动实现(代码中声明一个类)它是一个拓展接口的 Adaptive 拓展实现类。目前 Dubbo 项目里,只有 ExtensionFactory 拓展的实现类 AdaptiveExtensionFactory 有这么用。
- 第二种,标记在拓展接口的方法上,代表自动生成代码实现该接口的 Adaptive 拓展实现类(参考:[「4.5.4 createAdaptiveExtensionClassCode」](# 4.5.4 createAdaptiveExtensionClass))。
- value,从 Dubbo URL 获取参数中,使用键名(Key),获取键值。该值为真正的拓展名。
- 自适应拓展实现类,会获取拓展名对应的真正的拓展对象。通过该对象,执行真正的逻辑。
- 可以设置多个键名(Key),顺序获取直到有值。若最终获取不到,使用默认拓展名。
- 在 「4.5.4 createAdaptiveExtensionClassCode」 详细解析。
- value,从 Dubbo URL 获取参数中,使用键名(Key),获取键值。该值为真正的拓展名。
七. @Activate
org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.Activate,自动激活条件的标记。代码如下:
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface Activate {
/**
* Activate the current extension when one of the groups matches. The group passed into
* {@link ExtensionLoader#getActivateExtension(URL, String, String)} will be used for matching.
*
* @return group names to match
* @see ExtensionLoader#getActivateExtension(URL, String, String)
*/
/**
* Group过滤条件。
* <br />
* 包含{@link ExtensionLoader#getActivateExtension}的group参数给的值,则返回扩展。
* <br />
* 如没有Group设置,则不过滤。
*/
String[] group() default {};
/**
* Activate the current extension when the specified keys appear in the URL's parameters.
* <p>
* For example, given <code>@Activate("cache, validation")</code>, the current extension will be return only when
* there's either <code>cache</code> or <code>validation</code> key appeared in the URL's parameters.
* </p>
*
* @return URL parameter keys
* @see ExtensionLoader#getActivateExtension(URL, String)
* @see ExtensionLoader#getActivateExtension(URL, String, String)
*/
/**
* Key过滤条件。包含{@link ExtensionLoader#getActivateExtension}的URL的参数Key中有,则返回扩展。
* <p/>
* 示例:<br/>
* 注解的值 <code>@Activate("cache,validatioin")</code>,
* 则{@link ExtensionLoader#getActivateExtension}的URL的参数有<code>cache</code>Key,或是<code>validatioin</code>则返回扩展。
* <br/>
* 如没有设置,则不过滤。
*/
String[] value() default {};
/**
* Relative ordering info, optional
* Deprecated since 2.7.0
*
* @return extension list which should be put before the current one
*/
/**
* 排序信息,可以不提供。
*/
@Deprecated
String[] before() default {};
/**
* Relative ordering info, optional
* Deprecated since 2.7.0
*
* @return extension list which should be put after the current one
*/
/**
* 排序信息,可以不提供。
*/
@Deprecated
String[] after() default {};
/**
* Absolute ordering info, optional
*
* @return absolute ordering info
*/
/**
* 排序信息,可以不提供。
*/
int order() default 0;
}
- 对于可以被框架中自动激活加载扩展,
@Activate用于配置扩展被自动激活加载条件。比如,Filter 扩展,有多个实现,使用@Activate的扩展可以根据条件被自动加载。 - 分成过滤条件和排序信息两类属性,大家可以看下代码里的注释。
- 在 [「4.6 获得激活的拓展对象数组」](#4.6 获得激活的拓展对象数组) 详细解析。
八. ExtensionFactory
org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.ExtensionFactory,拓展工厂接口。代码如下:
/**
* ExtensionFactory
*
* 拓展工厂接口
*/
@SPI
public interface ExtensionFactory {
/**
* Get extension.
*
* 获得拓展对象
*
* @param type object type. 拓展接口
* @param name object name. 拓展名
* @return object instance. 拓展对象
*/
<T> T getExtension(Class<T> type, String name);
}
- ExtensionFactory 自身也是拓展接口,基于 Dubbo SPI 加载具体拓展实现类。
#getExtension(type, name)方法,在 [「4.4.3 injectExtension」](#4.4.3 injectExtension) 中,获得拓展对象,向创建的拓展对象注入依赖属性。在实际代码中,我们可以看到不仅仅获得的是拓展对象,也可以是 Spring 中的 Bean 对象。- ExtensionFactory 子类类图如下:
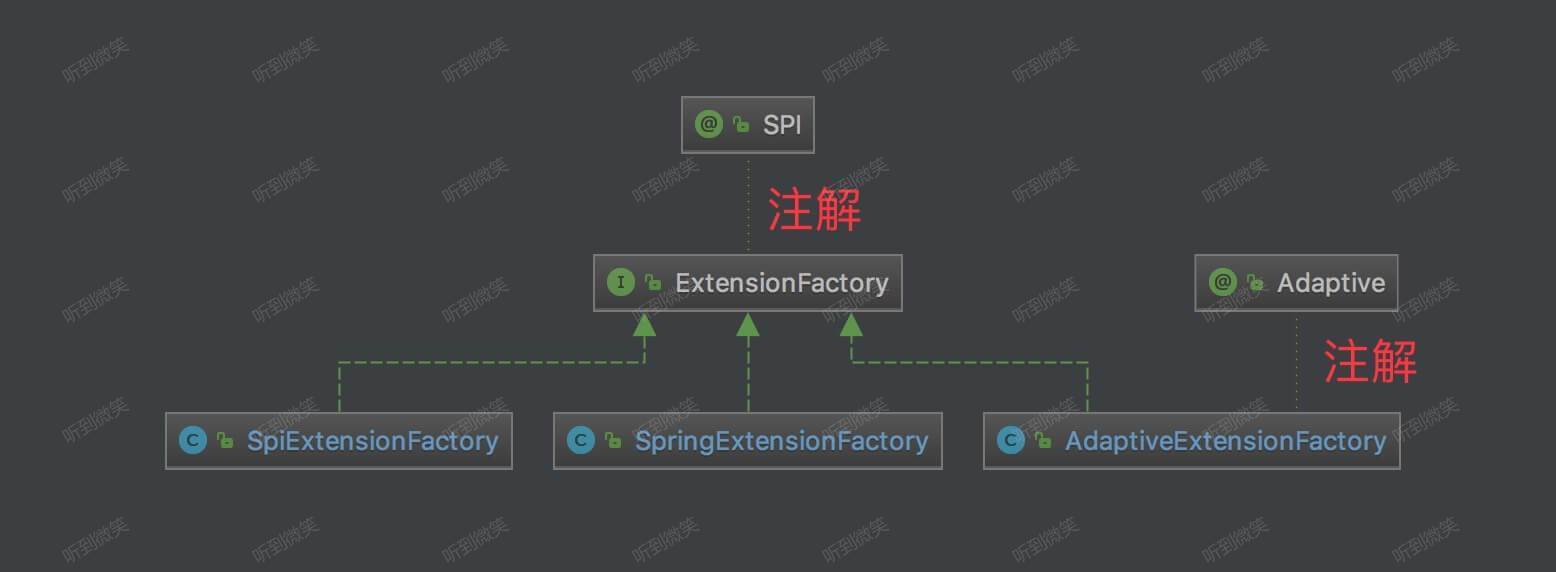
8.1 AdaptiveExtensionFactory
org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.factory.AdaptiveExtensionFactory,自适应 ExtensionFactory 拓展实现类。代码如下:
@Adaptive
public class AdaptiveExtensionFactory implements ExtensionFactory {
/**
* ExtensionFactory 拓展对象集合
*/
private final List<ExtensionFactory> factories;
public AdaptiveExtensionFactory() {
// 使用 ExtensionLoader 加载拓展对象实现类。
ExtensionLoader<ExtensionFactory> loader = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ExtensionFactory.class);
List<ExtensionFactory> list = new ArrayList<ExtensionFactory>();
for (String name : loader.getSupportedExtensions()) {
list.add(loader.getExtension(name));
}
factories = Collections.unmodifiableList(list);
}
@Override
public <T> T getExtension(Class<T> type, String name) {
// 遍历工厂数组,直到获得到属性
for (ExtensionFactory factory : factories) {
T extension = factory.getExtension(type, name);
if (extension != null) {
return extension;
}
}
return null;
}
}
@Adaptive注解,为 ExtensionFactory 的自适应拓展实现类。- 构造方法,使用 ExtensionLoader 加载 ExtensionFactory 拓展对象的实现类。若胖友没自己实现 ExtensionFactory 的情况下,
factories为 SpiExtensionFactory 和 SpringExtensionFactory 。 #getExtension(type, name)方法,遍历factories,调用其#getExtension(type, name)方法,直到获得到属性值。
8.2 SpiExtensionFactory
org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.factory.SpiExtensionFactory,SPI ExtensionFactory 拓展实现类。代码如下:
public class SpiExtensionFactory implements ExtensionFactory {
/**
* 获得拓展对象
*
* @param type object type. 拓展接口
* @param name object name. 拓展名
* @param <T> 泛型
* @return 拓展对象
*/
@Override
public <T> T getExtension(Class<T> type, String name) {
if (type.isInterface() && type.isAnnotationPresent(SPI.class)) {// 校验是 @SPI
// 加载拓展接口对应的 ExtensionLoader 对象
ExtensionLoader<T> loader = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(type);
// 加载拓展对象
if (!loader.getSupportedExtensions().isEmpty()) {
return loader.getAdaptiveExtension();
}
}
return null;
}
}
8.3 SpringExtensionFactory
org.apache.dubbo.config.spring.extension.SpringExtensionFactory,Spring ExtensionFactory 拓展实现类。代码如下:
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.dubbo.config.spring.extension;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.ExtensionFactory;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.SPI;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.logger.Logger;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.logger.LoggerFactory;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.utils.ConcurrentHashSet;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import java.util.Set;
import static org.apache.dubbo.config.spring.util.DubboBeanUtils.getOptionalBean;
/**
* SpringExtensionFactory
*/
public class SpringExtensionFactory implements ExtensionFactory {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SpringExtensionFactory.class);
/**
* Spring Context 集合
*/
private static final Set<ApplicationContext> CONTEXTS = new ConcurrentHashSet<ApplicationContext>();
public static void addApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) {
CONTEXTS.add(context);
if (context instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext) {
((ConfigurableApplicationContext) context).registerShutdownHook();
}
}
public static void removeApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) {
CONTEXTS.remove(context);
}
public static Set<ApplicationContext> getContexts() {
return CONTEXTS;
}
// currently for test purpose
public static void clearContexts() {
CONTEXTS.clear();
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getExtension(Class<T> type, String name) {
//SPI should be get from SpiExtensionFactory
if (type.isInterface() && type.isAnnotationPresent(SPI.class)) {
return null;
}
for (ApplicationContext context : CONTEXTS) {
// 获得属性
T bean = getOptionalBean(context, name, type);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
//logger.warn("No spring extension (bean) named:" + name + ", try to find an extension (bean) of type " + type.getName());
return null;
}
}
例子:
DemoFilter 是笔者实现的 Filter 拓展实现类,代码如下:
public class DemoFilter implements Filter {
private DemoDAO demoDAO;
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
public DemoFilter setDemoDAO(DemoDAO demoDAO) {
this.demoDAO = demoDAO;
return this;
}
}
-
DemoDAO ,笔者在 Spring 中声明对应的 Bean 对象。
<bean id="demoDAO" class="com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.provider.DemoDAO" /> -
在 「4.4.3 injectExtension」 中,会调用
#setDemoDAO(demo)方法,将 DemoFilter 依赖的属性demoDAO注入。
本文参考至:
