一. timeout 与 retries
Dubbo的服务可以通过timeout配置超时时间,防止远程调用失败,该属性的默认值为1000(ms),用户可以在多个地方配置服务的超时时间:
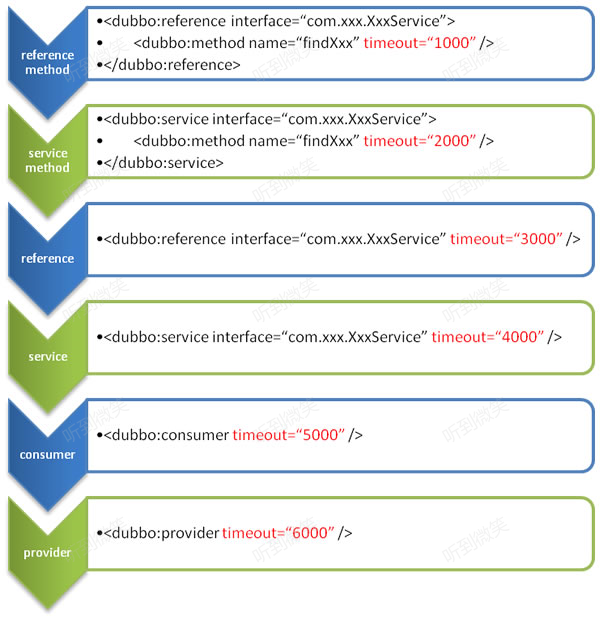
图中涉及的配置方式从上至下优先级越来越低,总体来说配置覆盖遵循以下规律:consumer配置优先于provider配置,细粒度配置优先于整体配置。
我们在消费者中sleep一段时间人为制造超时效果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| @DubboService(timeout = 3000)
@Slf4j
public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService{
@Override
public UserDTO queryById(Integer userId) {
if (userId == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("参数不能为空");
}
log.info("remote call queryById");
User user = userMapper.selectById(userId);
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return modelToDto(user);
}
}
|
当我们消费者调用该服务时会出现超时异常:
1
| UserDTO userDTO = userService.queryById(1);
|
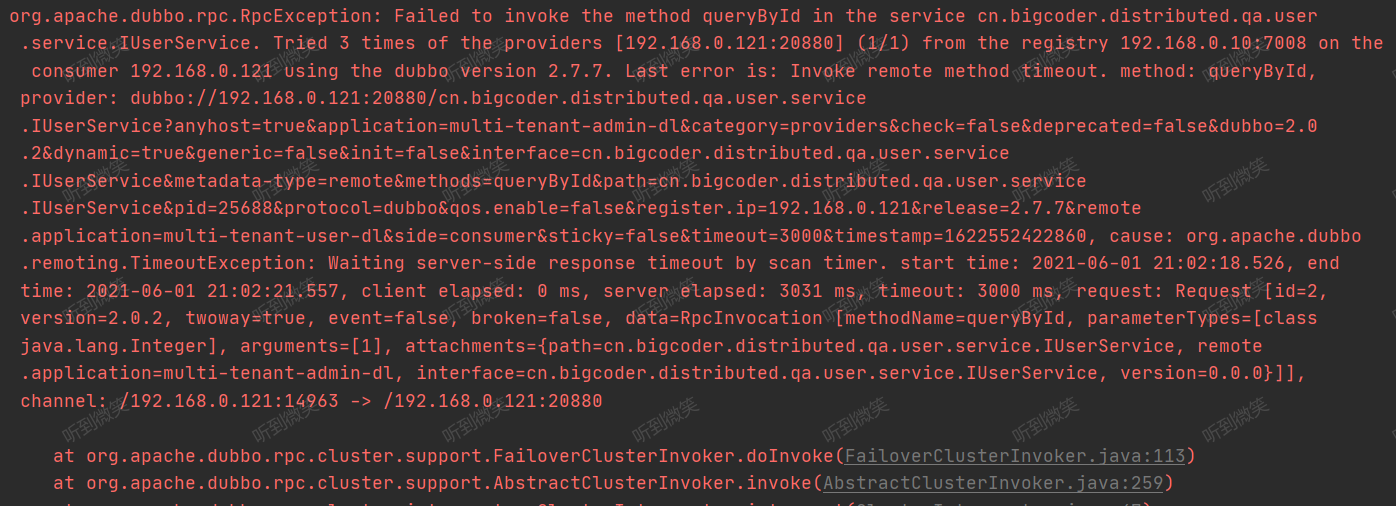
我们查看服务提供者的控制台,可以发现服务提供者被触发了3次:

在Dubbo中有一个参数retries,它表示消费者在调用远程服务时,出现超时等RpcException时会去最多重试调用N次服务,默认情况下retries=2这也是为什么在出现超时调用后,服务端会调用三次。
二. 集群容错机制
失败重试机制,在官方文档中称为集群容错。
2.1 集群容错机制分类
Dubbo官方提供了多种失败重试机制,缺省值是failover。
- Failover Cluster:失败自动切换,当出现失败,重试其它服务器。通常用于读操作,但重试会带来更长延迟。可通过
retries="2" 来设置重试次数(不含第一次)。
- Failfast Cluster:快速失败,只发起一次调用,失败立即报错。通常用于非幂等性的写操作,比如新增记录。但是这里也会有问题的,如果是因为网络问题,Provider的响应时间慢,Consumer以为调用失败了,但是Provider却调用成功了,涉及到分布式事务的问题。
- Failsafe Cluster:失败安全,出现异常时,直接忽略。通常用于写入审计日志等操作。
- Failback Cluster:失败自动恢复。调用失败后,consumer不会重试,而是把这个消息丢到provider的重试的线程池里面,定时的重试调用一定的次数,调用失败写日志
- Forking Cluster:并行调用多个服务器,只要一个成功即返回。通常用于实时性要求较高的读操作,但需要浪费更多服务资源。可通过
forks="2" 来设置最大并行数。
- Broadcast Cluster:广播调用所有提供者,逐个调用,任意一台报错则报错。通常用于通知所有提供者更新缓存或日志等本地资源信息。现在广播调用中,可以通过
broadcast.fail.percent 配置节点调用失败的比例,当达到这个比例后,BroadcastClusterInvoker 将不再调用其他节点,直接抛出异常。broadcast.fail.percent取值在 0~100 范围内。默认情况下当全部调用失败后,才会抛出异常。 broadcast.fail.percent 只是控制的当失败后是否继续调用其他节点,并不改变结果(任意一台报错则报错)。broadcast.fail.percent 参数 在 dubbo2.7.10 及以上版本生效。
2.1 集群模式的配置
注解配置
1
| @reference(cluster = "broadcast", parameters = {"broadcast.fail.percent", "20"})
|
XML配置
1
2
| <dubbo:service cluster="failsafe" />
<dubbo:reference cluster="failsafe" />
|
三. Failover Cluster
Dubbo默认使用的是Failover Cluster机制,如果不清楚这一机制那么写出的代码会有很多隐患。
服务的超时是开发人员不好控制的,如果某些时候因为机器负载波动导致一个写操作服务发生超时重试,那么就会出现重复写的问题,导致脏数据的产生。
Failover Cluster官方建议在读环境下使用,但是奈何很多同学都没有注意到这一点。

Failover Cluster的实现在org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.support.FailoverClusterInvoker:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
| public class FailoverClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FailoverClusterInvoker.class);
public FailoverClusterInvoker(Directory<T> directory) {
super(directory);
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, final List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
List<Invoker<T>> copyInvokers = invokers;
checkInvokers(copyInvokers , invocation);
String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
int len = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, RETRIES_KEY, DEFAULT_RETRIES) + 1;
if (len <= 0) {
len = 1;
}
RpcException le = null;
List<Invoker<T>> invoked = new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(copyInvokers.size());
Set<String> providers = new HashSet<String>(len);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (i > 0) {
checkWhetherDestroyed();
copyInvokers = list(invocation);
checkInvokers(copyInvokers, invocation);
}
Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, copyInvokers, invoked);
invoked.add(invoker);
RpcContext.getContext().setInvokers((List) invoked);
try {
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
if (le != null && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Although retry the method " + methodName
+ " in the service " + getInterface().getName()
+ " was successful by the provider " + invoker.getUrl().getAddress()
+ ", but there have been failed providers " + providers
+ " (" + providers.size() + "/" + copyInvokers.size()
+ ") from the registry " + directory.getUrl().getAddress()
+ " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost()
+ " using the dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ". Last error is: "
+ le.getMessage(), le);
}
return result;
} catch (RpcException e) {
if (e.isBiz()) {
throw e;
}
le = e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
le = new RpcException(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
providers.add(invoker.getUrl().getAddress());
}
}
throw new RpcException(le.getCode(), "Failed to invoke the method "
+ methodName + " in the service " + getInterface().getName()
+ ". Tried " + len + " times of the providers " + providers
+ " (" + providers.size() + "/" + copyInvokers.size()
+ ") from the registry " + directory.getUrl().getAddress()
+ " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " using the dubbo version "
+ Version.getVersion() + ". Last error is: "
+ le.getMessage(), le.getCause() != null ? le.getCause() : le);
}
}
|